Featured
What Is The Phase Of A Waveform
What Is The Phase Of A Waveform. We measure phase in degrees or radians, from 0° to 360° or 0 radians to 2π radians. A general form of a sinusoidal wave is y (x,t)=asin (kx−ωt+ϕ) y ( x , t ) = a sin ( kx − ω t + ϕ ) , where a is the amplitude of the wave, ω is the wave’s angular frequency, k is the wavenumber, and ϕ is the phase of the sine wave given in radians.
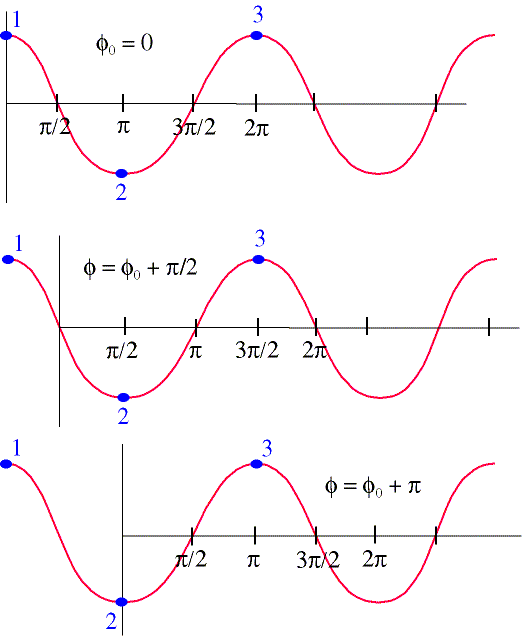
The leading phase represents that the wave is ahead of another one having the same frequency. The phase of a sine wave can be understood as the horizontal position of a waveform with respect to one cycle. The phase is expressed in terms of radians.
Designs Can Be Found In The Literature To Lower Both Integrated And Peak
When two or more waves of the same frequency are interfering in a medium or made to travel in the same path, then the “phase” of waves play an important role to produce the desired output without any noise. One radian of phase equals approximately 57.3°. The individual phases are separated from each other by an angle of 120 degrees.
Phase Ii Is The Beginning Of Expiration Which Occurs When The Anatomic Dead Space And Alveolar Gas From The Alveoli/Bronchioles Transition.
The leading phase represents that the wave is ahead of another one having the same frequency. A general form of a sinusoidal wave is y (x,t)=asin (kx−ωt+ϕ) y ( x , t ) = a sin ( kx − ω t + ϕ ) , where a is the amplitude of the wave, ω is the wave’s angular frequency, k is the wavenumber, and ϕ is the phase of the sine wave given in radians. The phase of a sine wave can be understood as the horizontal position of a waveform with respect to one cycle.
The Complete Phase Of A Full Cycle Of A Waveform Is 360 0.
Any sine wave that does not pass through zero at t = 0 has a phase shift. A normal waveform has four different phases: Mismatched filters, therefore, have been proposed for use with pc waveforms to lower time sidelobes.
Phase Can Also Be An Expression Of Relative Displacement Between Or Among Waves Having The Same Frequency.
The pc waveform has large phase discontinuities which preclude the use of windowing with an appropriate weighting function to reduce time sidelobes. Any complex waveform is made up of several superimposed harmonics of the form a sin(ωt + φ), where a is the amplitude, ω is the frequency, t is time, and φ is phase. The phase is expressed in terms of radians.
Looking At The Diagram Below, It Can Be Seen That The Instantaneous Phase Of The Waveform With Respect To The Start Is The Angle That Is Angle That Is Between The Start Of The Waveform And The Current Position.
Phase is the position of a point in time (an instant) on a waveform cycle. A complete cycle is 360°. A complete cycle is defined as the interval required for the waveform to return to its arbitrary initial value.
Comments
Post a Comment